This article describes an information set to map and mannequin research collaborations in German biotechnology.
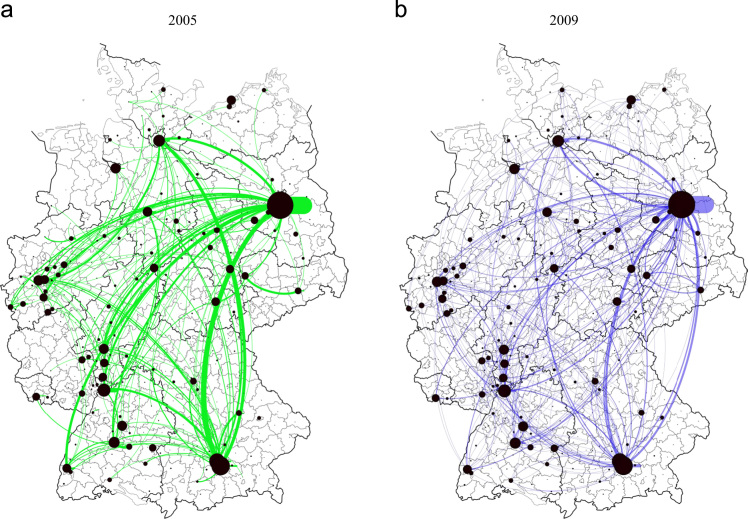
Underlying micro-data for companies and establishments in the biotech sector along with data on their research collaboration companions have been extracted from a industrial industry directory, the BIOCOM Year and Address guide, for 2005 and 2009.
The information have been processed and aggregated to the extent of NUTS3 areas. This core information set has been linked to regional covariates which measure the regional endowment with biotech-related research capacities, sector-specific S&T coverage assist and the power of a area׳s general native innovation system.
The full information set, which is hooked up to this text, provides utilized researchers an alternate supply of data for empirical analyses of information flows in research networks and for finding out their determinants.
Potential fields of utility embody social community and regression evaluation. First empirical outcomes are reported in “Determining elements of interregional research collaboration in Germany׳s biotech community: Capacity, proximity, coverage?” (Mitze and Strotebeck, 2018) and “Centrality and get-richer mechanisms in interregional data networks” (Mitze and Strotebeck, 2018).
Distinct options of rabbit and human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells: implications for biotechnology and translational research.
UNASSIGNEDOwing to their similarity with people, rabbits are helpful for a number of functions in biotechnology and translational research from primary to preclinical research.
In this sense, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are recognized for his or her therapeutic potential and promising future in regenerative medication. As many research have been using rabbit adipose-derived MSCs (ASCs) as a mannequin of human ASCs (hASCs), it’s basic to check their traits and perceive how distinct options may have an effect on the interpretation to human medication.
UNASSIGNEDThe purpose of this examine was to comparatively characterize rabbit ASCs (rASCs) and hASCs to additional makes use of in biotechnology and translational research.UNASSIGNEDrASCs and hASCs had been remoted and characterised by their immunophenotype, differentiation potential, proliferative profile, and nuclear stability in vitro.
UNASSIGNEDBoth ASCs introduced differentiation potential to osteocytes, chondrocytes, and adipocytes and shared comparable immunophenotype expression to CD105+, CD34-, and CD45-, however rabbit cells expressed considerably decrease CD73 and CD90 than human cells. In addition, rASCs introduced larger clonogenic potential and proliferation fee than hASCs however no distinction in nuclear alterations.
UNASSIGNEDThe distinct options of rASCs and hASCs can positively or negatively have an effect on their use for various functions in biotechnology (reminiscent of cell reprogramming) and translational research (reminiscent of cell transplantation, tissue engineering, and pharmacokinetics).
Nevertheless, the particularities between rabbit and human MSCs mustn’t stop rabbit use in preclinical fashions, however care must be taken to interpret outcomes and correctly translate animal findings to medication.

